Investigated were 56 severely epileptic ill patients in a special hospital for epilepsy.
In the experimental group 34 of these patients received in addition to the conventional therapies a treatment with Medical Resonance Therapy Music®, and in the control group 22 patients received the conventional drug treatment only.
The psychological investigations were performed by the help of the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory (MMPI).
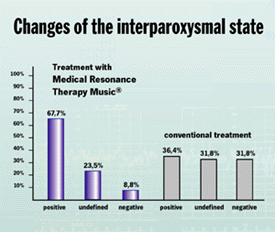
Changes in the interparoxysmal state were documented in 67,7% of the patients of this group as positive, in 23,5% as undefined and in 8,8% as negative. Most sensitive for the positive effects of the Medical Resonance Therapy Music® were the following MMPI-parameters:
- asthenic traits
- paranoid traits
- hypochondria
- aggressiveness
- depressive states
- and the general degree
of the illness
In this group the changes of the interparoxysmal state were recorded in 36,4% of the observations as positive, in 31,8% as undefined and in 31,8% as negative.
Investigators:
Dr. med. T. J. Teterkina
Dr. med. W. Sidorenko
Dr. med. A. S. Fedulow
Dr. med. G. A. Lukaschewitsch
Dr. med. G. W. Massalski